The 5R strategy: Transform your waste and reduce costs
- Arnaud
- 9 minutes reading

You have surely been aware for some time now that natural resources are becoming increasingly scarce, and as climate challenges intensify, businesses have every incentive to rethink their production and consumption methods.
The linear model “Extract – Produce – Dispose” must give way to a more virtuous approach: the circular economy. Among the most recognized approaches within this circular economy is the 5R method: Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Rot.
This article, intended as a reference for all professionals and enthusiasts of the circular economy, outlines the origins of the 5R, their significance, and most importantly how to implement them. In particular, it highlights internal or external marketplace solutions that facilitate the recovery of both primary and secondary raw materials in line with the latest regulations.
- Where do the 5Rs come from?
- What do the 5Rs mean?
- Why adopt the 5Rs in business?
- What are the five steps of the 5R method?
- How to apply the 5R method to your corporate waste?
- How to apply the 5R method to the creation of new products?
- Revalorizing primary and secondary materials through the marketplace model
- Solutions for businesses
- Internal marketplace
- External marketplace (C2C, B2B, C2B2C)
- C2B2C marketplace with corporate oversight
- Transforming and revalorizing production waste via an internal marketplace
- Real-world examples of revalorization within the same group
- Transforming winemaking residues into “plant-based leather”
- Manufacturing furniture and repurposing wood shavings
- The tangible benefits of this approach
- Practical tips for a successful 5R transition
1. Where do the 5Rs come from?
The origins of the 5R concept lie in the zero-waste movement and the circular economy. Initially introduced and popularized by American environmental activist Bea Johnson (“Zero Waste”) and subsequently adopted in numerous academic and institutional studies, the method was originally aimed at individual consumers.
However, these principles have naturally extended to businesses, whose environmental impact is significant. Today, the 5R strategy serves as a foundational methodology for adopting more responsible practices across both the industrial and service sectors.
2. What do the 5Rs mean?
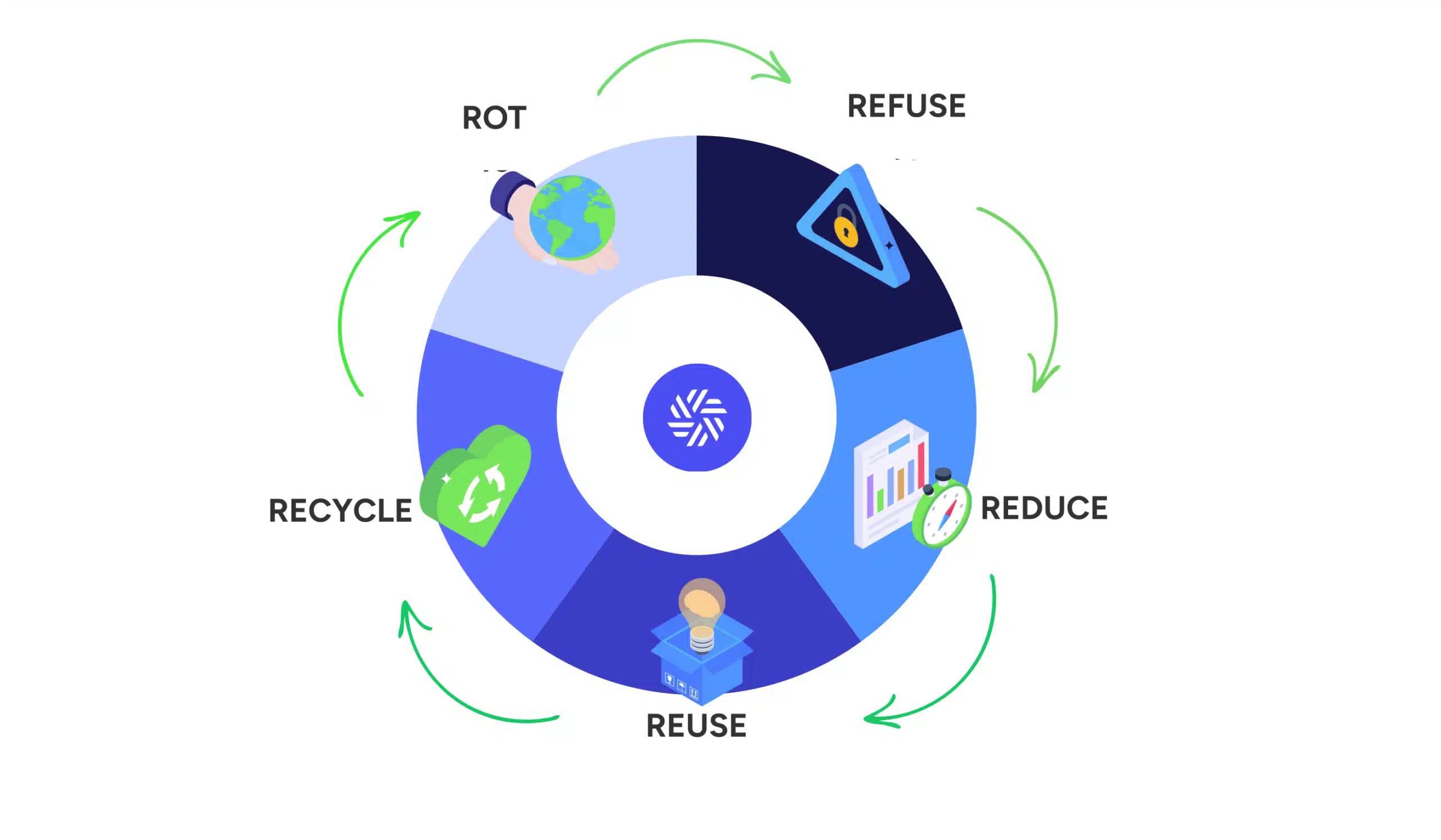
1. REFUSE
This involves saying “no” to products or services that are non-essential, generate unnecessary waste, or fail to align with ethical and environmental values. In a business setting, this can translate into rejecting untraceable raw materials, single-use products, or polluting production methods.
2. REDUCE
After refusing what isn’t necessary, the goal is to minimize the amount of resources used. This may involve optimizing processes, limiting packaging, or choosing more energy-efficient transportation methods. The ultimate aim is to lower both your ecological footprint and associated costs.
3. REUSE
Extend the lifespan of objects, components, or materials. Instead of throwing them away, opt for reuse or repair. In an industrial setting, this can involve refurbishing equipment or selling spare parts to other facilities or subsidiaries.
4. RECYCLE
If a product or material can no longer serve its original function, repurpose it for a different use. This principle underpins recycling: for instance, converting wood residues into bags of wood chips or transforming agri-food waste into bioplastics.5. ROT
Finally, anything that cannot be recycled or reused (and is organic or biodegradable) should be returned to the earth without causing harm. This includes composting or the natural decomposition of organic waste, thereby contributing to the regeneration of ecosystems.
Ready to turn your B2B, B2C, or C2C marketplace vision into reality?
To help you develop the best platform possible, we’ve gathered all the must-have features, key technical considerations, and best practices in a comprehensive document:
Download the Specifications template 🗒
Perfect for smaller or medium-scale projects without a formal purchasing process. It will help you outline your requirements effectively and streamline your selection process.
Download the Request for Proposal template 📒
Ideal for larger, more complex marketplace projects with a formal purchasing department or advanced procurement policies.
3. Why adopt the 5Rs in business?
Cost and risk reduction: By applying the 5R strategy, businesses can limit their resource expenses, reduce dependence on raw materials, and enhance resilience against price fluctuations.
Regulatory compliance: In France, the AGEC Law (Anti-Waste for a Circular Economy) imposes new environmental requirements. The 5R framework aligns perfectly with these legal obligations.
Enhanced brand image: A company committed to eco-responsibility benefits from a stronger reputation and better meets the growing expectations of its consumers and partners.
Innovation and competitiveness: Implementing circular initiatives fosters team creativity and generates new business models (rental, second-hand sales, co-production, etc.).
4. What are the five steps of the 5R strategy?
When we follow the chronology of decisions to be made, they can be organized as follows during product design:
- Refuse: Evaluate actual needs, audit suppliers, and reject unnecessary or non-responsible supplies.
- Reduce: Implement Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure consumption (water, energy, materials), design less energy-intensive processes, and train staff in eco-friendly practices.
- Reuse: Introduce an internal marketplace allowing workshops to sell or acquire used but still functional products.
- Recycle: Establish recycling channels, sign contracts with eco-organizations, promote internal waste recovery, and ensure waste traceability.
- Rot: Create composting zones and develop controlled biodegradation processes for organic materials.
5. How to apply the 5R method to your corporate waste?
1. Map your waste
The first step is to conduct a detailed diagnosis of your waste streams: Can you identify the source of the waste? Can you categorize the types of materials (plastic, wood, glass, metals, organic, etc.)? And finally, can you assess the volume and costs associated with this waste? Once you have answers to these questions, you can create a waste map and move on to prioritizing actions.
2. Prioritize actions according to the 5R principle
- Refuse: Eliminate avoidable waste upstream (excessive packaging, single-use consumables).
- Reduce: Optimize production and logistics processes (just-in-time production, document digitization, etc.).
- Reuse: Implement an internal platform for exchanging surplus materials and used equipment between workshops, departments, or subsidiaries.
- Recycle: Ensure that each waste stream has an appropriate recycling channel (paper, metals, etc.) and establish contracts with specialized partners if needed.
- Rot: Direct organic waste toward biological recovery methods (composting, anaerobic digestion).
Origami Marketplace has already worked with major players in the luxury goods sector, as well as in other industries, on this type of project. Thanks to our expertise, we can guide you towards the best practices adapted to the specificities and evolutions of your sector.

Antoine Mantel
→ Talk to our circular economy expert.
3. Implement waste traceability and reporting
Waste traceability is essential to measure the effectiveness of actions. Simultaneously, regular reporting (monthly, quarterly) keeps teams motivated and provides a foundation for future improvements.
6. How to apply the 5R method to the creation of new products?
Think eco-design. The 5R method applies right from the design phase:
- Refuse non-recyclable or high-carbon-impact materials.
- Reduce the amount of material used and extend the product’s lifespan.
- Reuse existing components (spare parts, production surpluses).
- Recycle manufacturing scraps systematically.
- Rot at the end of the product’s life, ensuring that biodegradable elements truly decompose.
Revalorize your primary and secondary materials through the marketplace model. In a circular design approach, raw materials and “waste” can become resources for other internal or external actors. This is where the marketplace comes in:
- Collection and listing: Residual materials (e.g., wood chips, grape skins, leather scraps) are listed on the internal platform or on a third-party portal (C2C, C2B2C).
- Availability: Other group workshops or partners can purchase or collect these materials for new projects (e.g., making benches, shoes, or derivative products).
- Valorization and additional revenue: Materials re-enter the value chain instead of becoming waste. The company benefits from additional income and adheres to sustainable practices aligned with the AGEC law.
7. Solutions for businesses
To go further, several configurations are possible:
A. An internal marketplace (Intragroup)
- Objective: Promote the exchange of raw materials, secondary materials, or equipment between different subsidiaries or workshops within the same group.
- Advantage: Full control by the company, simplified logistics flows, and material traceability.
- Result: Reduced procurement costs, lower waste production, and compliance with legal requirements.
B. An external marketplace (C2C, B2B, C2B2C)
- Objective: Provide the general public (C2C), other companies (B2B), or intermediaries (C2B2C) with access to repurposed materials or second-hand products.
- Advantage: Access to a broader market and promotion of reuse beyond the company’s scope.
- Result: New revenue streams and a strengthened brand image as a circular economy player.
C. A C2B2C platform with company control
- Objective: The company or a trusted third party inspects and verifies the condition and quality of products before reintroducing them into circulation.
- Advantage: Buyer security, adherence to quality standards, and reduced waste.
- Result: Customer loyalty, new profit streams, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
8. Transforming and revalorizing production waste via an internal marketplace
Here’s how a concrete process can be organized, inspired by observed use cases:
- Extraction and collection of raw materials: Raw materials (wood, grapes, leather, etc.) are harvested and listed on the marketplace.
- Production: During transformation (winemaking, woodworking, etc.), a final product is created (wine bottles, furniture, etc.) along with secondary materials (grape pomace powder, wood chips, leather scraps) and waste (residual waste).
- Recovery of waste: Instead of being discarded, these materials are recycled or repurposed (into vegetable oil, wood chip bags, tanning powder, etc.) and relisted on the internal marketplace.
- Reintegration into the production chain: Interested workshops (or even external partners) acquire these materials at a lower cost to create new products (shoes, public benches, accessories, etc.).
- Market launch: The finished products made from secondary materials can be sold either directly or through a new distribution channel (C2C, B2B, etc.). The company generates additional revenue while reducing its waste.
This virtuous cycle perfectly embodies the 5Rs and offers a strategic solution to eco-responsibility.
9. Real-world examples of revalorization within the same group
To better illustrate the 5R approach and the power of an internal marketplace, here are two examples of material flows in the industry:
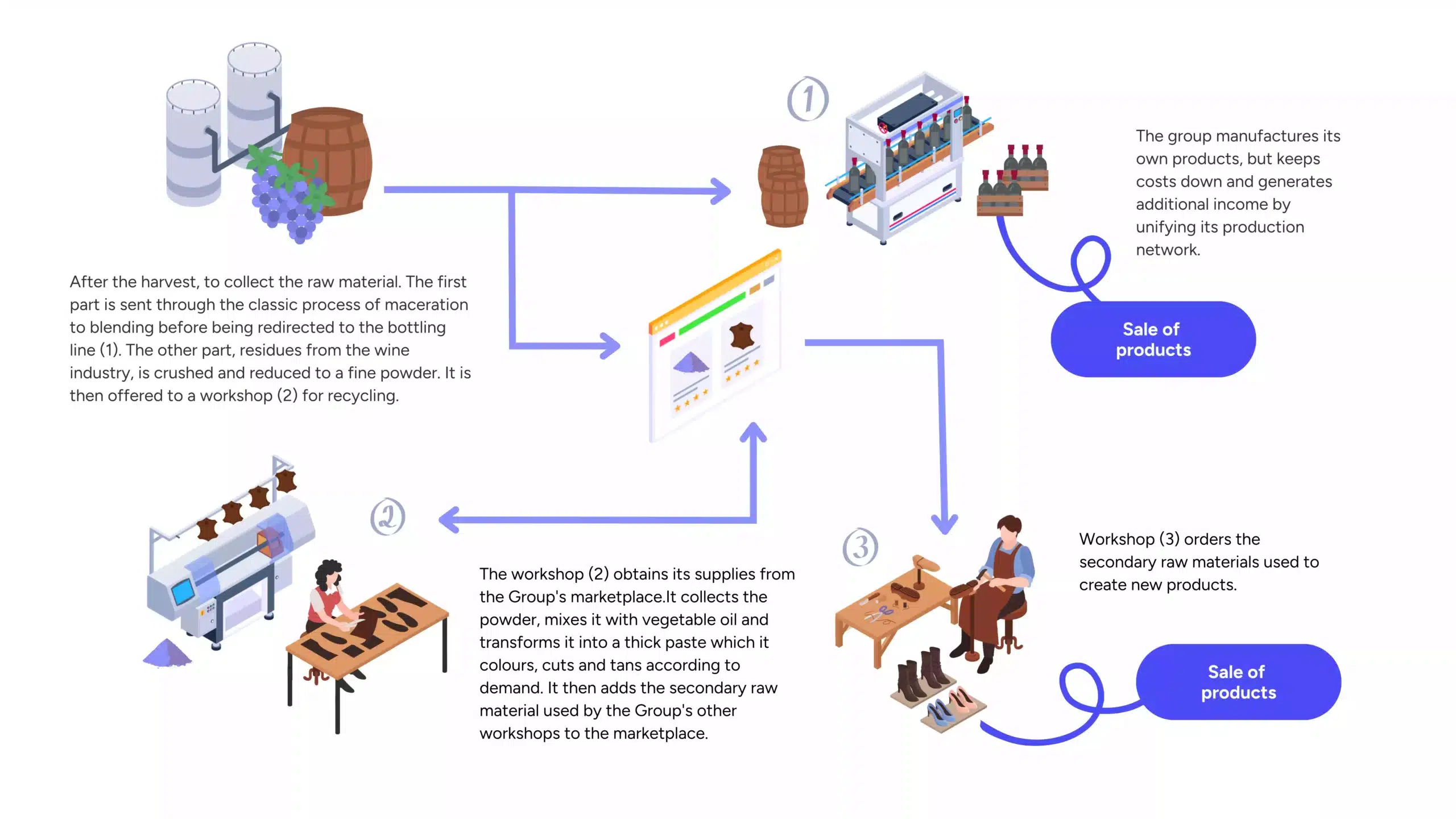
Transforming winemaking residues into plant-based leather:
- Harvest and winemaking: After the grape harvest, part of the grapes is used to produce wine (classic processes of maceration, blending, bottling, etc.). The residues (pomace, grape skins) are crushed and ground into a fine powder.
- Marketplace listing: These processed residues are offered as a secondary raw material on the internal platform.
- On-site revalorization: Another workshop acquires this powder, mixes it with vegetable oil, and obtains a thick paste that can be dyed, cut, and tanned as needed. The result resembles a plant-based leather that can be crafted into shoes, bags, or leather goods.
- Commercialization and additional revenue: The final products (shoes, plant-based leather accessories) are sold through the same marketplace or other channels. In doing so, the group repurposes what was once waste and creates a new source of income.
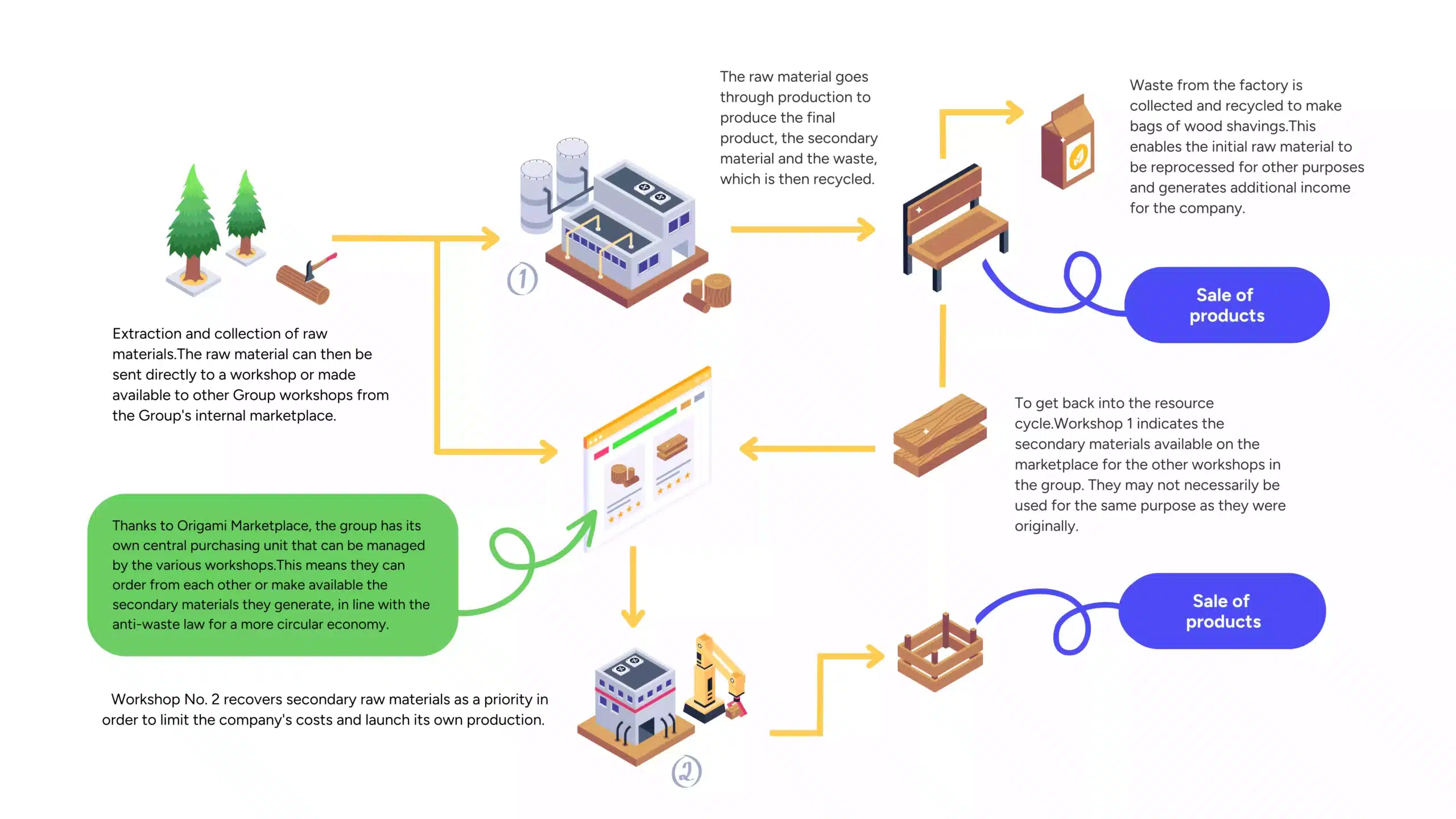
Manufacturing furniture and revalorizing wood chips:
- Wood extraction and collection: Tree trunks are transported to an initial workshop (sawmill) to be turned into planks destined for furniture or other products.
- Production and creation of a finished product: The workshop transforms the planks into benches, storage boxes, or furniture pieces. During production, secondary materials (wood scraps) and waste (chips) are generated.
- Waste valorization: The chips are collected, bagged, and sold (e.g., for garden mulch or fuel). Wood scraps are offered on the internal marketplace to serve as raw materials for other workshops (crafts, repairs, etc.).
- Reintegration into the chain: Workshop #2, for example, can order these scraps to manufacture smaller items (frames, utensils, etc.), thereby reducing costs. Each product made from these secondary materials is then sold, extending resource lifecycles and minimizing waste.
In these two examples, the marketplace acts as a catalyst:
- It centralizes information on available resources (primary and secondary materials).
- It facilitates reuse and recycling, either internally or with external stakeholders.
- It generates additional revenue while reducing the company’s ecological footprint.
Do you have a circular economy problem? We're here to advise you, free of charge. Simply make an appointment, and we'll share our expertise with you to identify the best solution for your needs. Together, let's find sustainable and effective solutions for your business! 🌱

Alexandre Duquenoy
→ Talk to our circular economy expert.
10. The tangible benefits of this approach
- Cost reduction: Lower expenses for raw materials and decreased storage and transportation costs, thanks to in-house logistics.
- Environmental protection: Less residual waste and a reduced carbon footprint.
- Compliance with AGEC Law: Anticipate regulatory obligations, recover waste, and combat overconsumption.
- Brand image: Positions the company as a leader in sustainable innovation, attracting new clients and retaining existing ones.
- Additional revenue: Sales of materials or products derived from what were once considered waste.
11. Practical tips for a successful 5R transition
- Involve all stakeholders: Management, workshop supervisors, logistics teams, etc. must be on board with the initiative.
- Digitize flow management: Centralize information on a single platform (marketplace) to streamline traceability and stock availability.
- Train and raise awareness: Conduct workshops and provide guides or checklists to support each department.
- Measure to improve: Define key performance indicators (reuse rate, volume of waste diverted from landfills, etc.) and set incremental targets.
- Communicate: Publicize the approach internally (newsletters, intranet, meetings) and externally (website, CSR reports, customer communications).
Adopting the 5R strategy (Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Rot) is no longer optional it has become an
essential lever for addressing today’s environmental and economic challenges. Beyond the direct benefits (cost reduction, legal compliance, and enhanced brand image), businesses that commit to this path gain
resilience and competitiveness.
In this evolution, implementing an internal or external marketplace proves to be a strategic tool to:
- Optimize the flow of primary and secondary materials,
- Facilitate reuse and recycling,
- Generate additional revenue,
- Comply with the AGEC law,
- Strengthen the environmental and social commitment across the entire production chain.
The 5Rs are only a starting point: they should form part of a broader circular economy and
continuous innovation strategy. Thanks to a high-performance SaaS solution like Origami Marketplace, businesses can transform their waste into genuine resources, achieve operational excellence, and make a lasting commitment to the ecological transition.
Besoin d’aller plus loin ?
- Contact Our Team to discover how to launch your own revalorization platform in less than 4 months.
- Explore the Solution and browse our numerous key features (multi-vendor, ad management, ordering with and without payment, etc.)
By adopting the 5Rs, you will make your resource management a true competitive advantage while contributing to the construction of a more responsible future. Discover how the Origami Marketplace API and its network of partners can transform your business through its innovative solution based on the marketplace model.

